

117 ✬) under a protective atmosphere of CO 2. Diethylzinc may be prepared and distilled (b.p. Simple alkyl derivatives of all three kinds are pyrophoric (burn spontaneously on exposure to air) and react with water to generate the corresponding alkane (RH) however, the zinc compounds are distinctly less reactive in other respects. R- X + 2 Li –––> R- Li + Li X An Alkyl Lithium Reagent 1917 W.

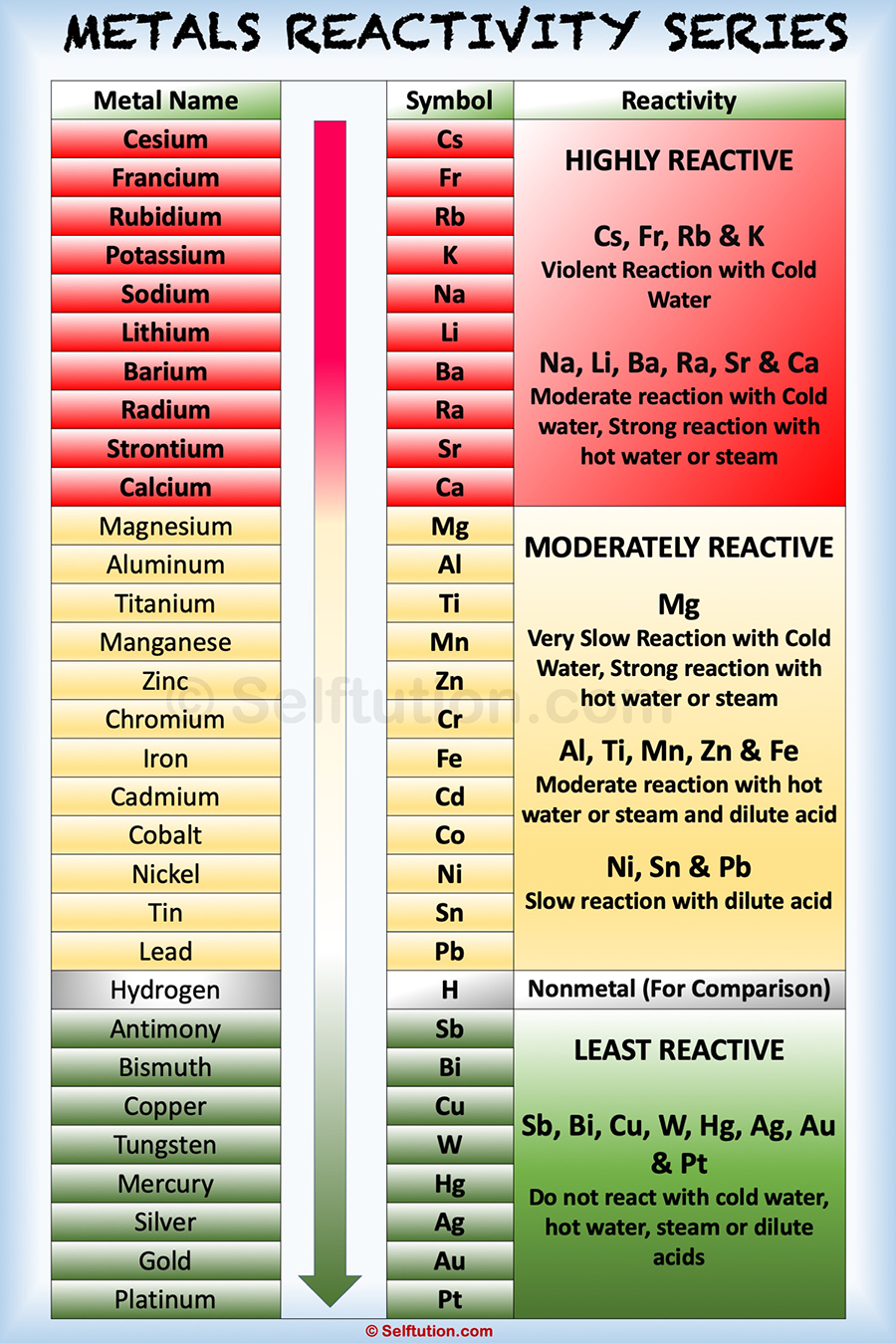
R- X + Mg –––> R- Mg -X A Grignard Reagent 1900 V. % Ionic Character of H 3 C – Metal (CH 3) 2Hg R- Zn- X An Alkyl Zinc Reagent 1850 E. In general, the reactivity parallels the ionic character of the carbon-metal bond, which may be estimated from the proton and carbon chemical shifts of methyl derivatives. Depending on the reduction potential of the metal, the reactivity of organometallic compounds varies markedly, the most reactive requiring low to moderate temperatures and inert conditions (atmosphere and solvents) for preparation and use. Such compounds have been known and studied for nearly 200 years, and their unique properties have been widely used to effect synthetic transformations. Organic compounds incorporating carbon-metal bonds are called organometallic compounds.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
